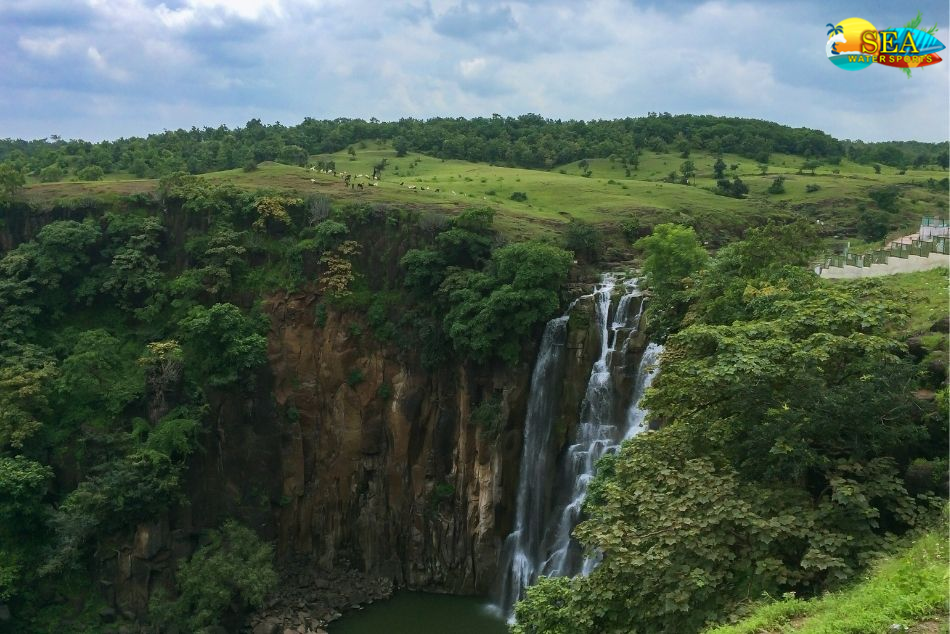
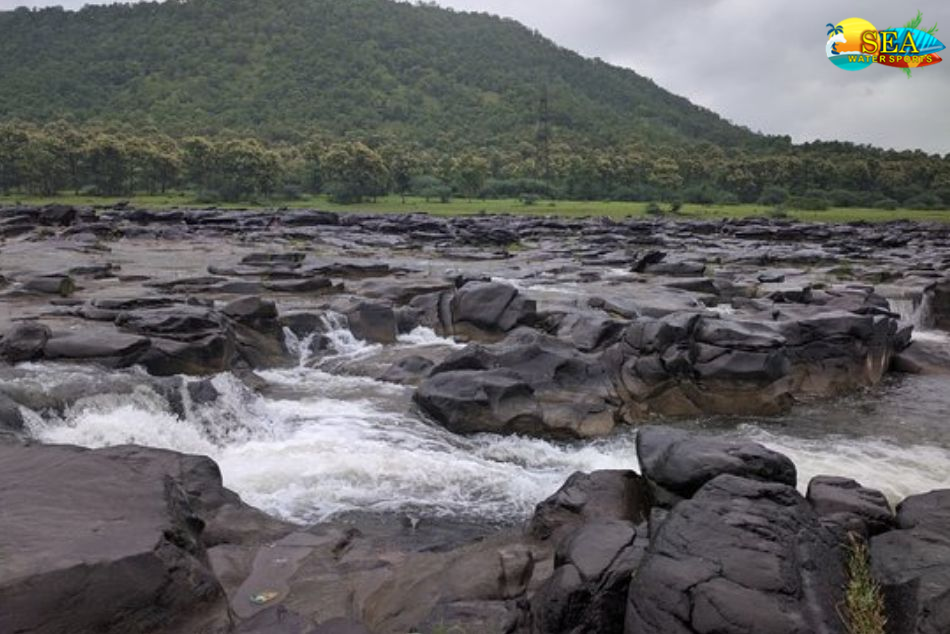
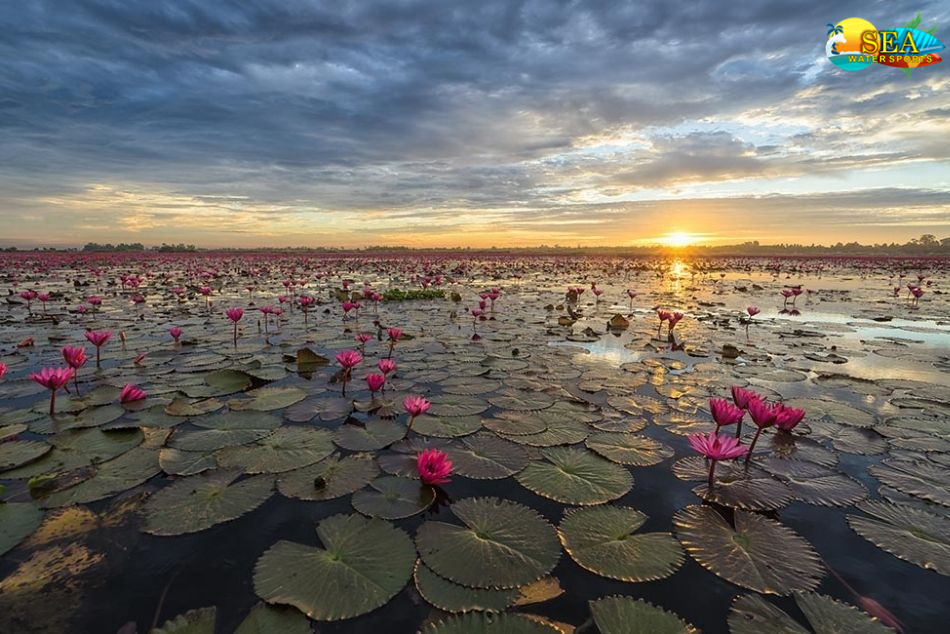
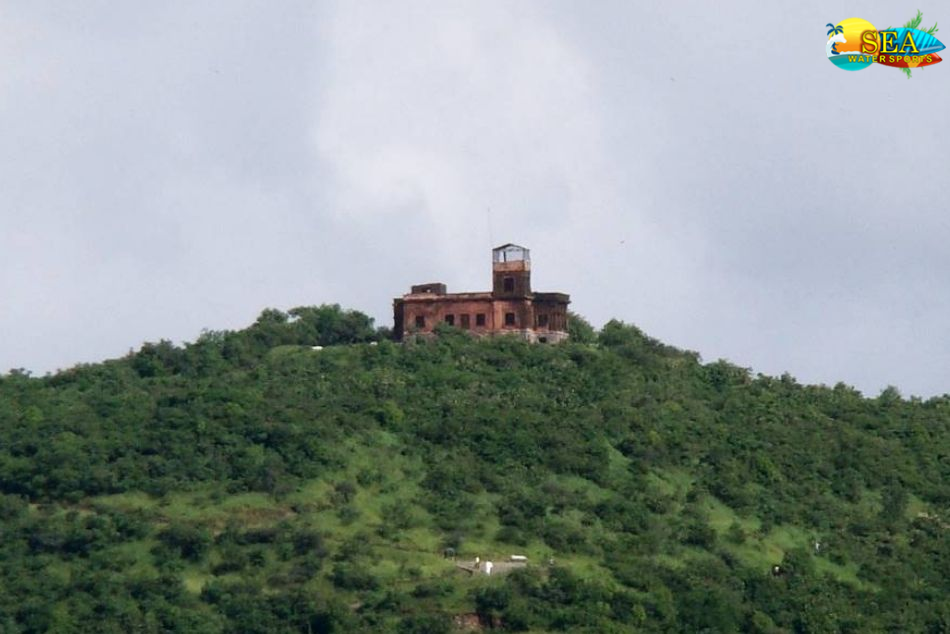
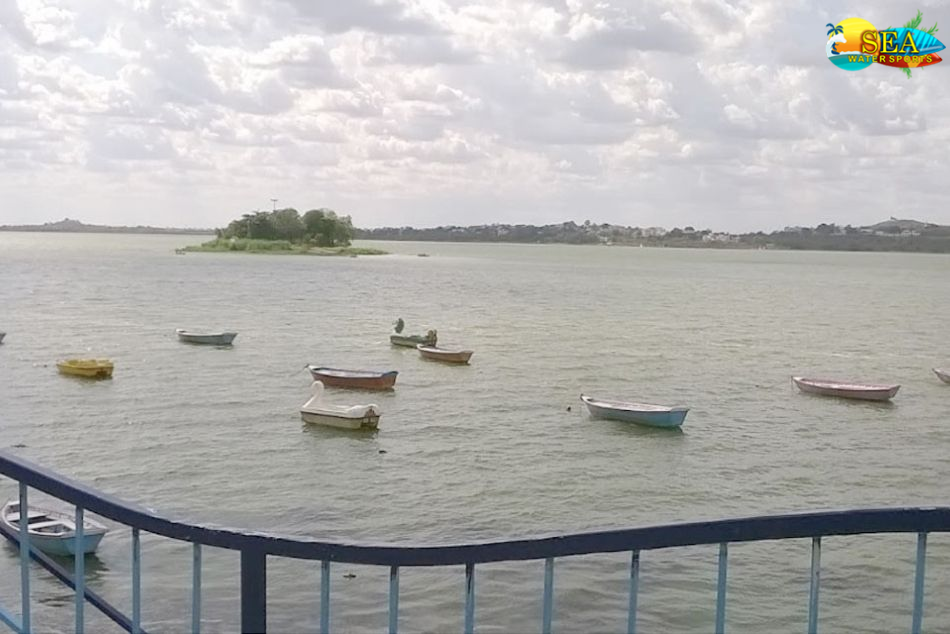
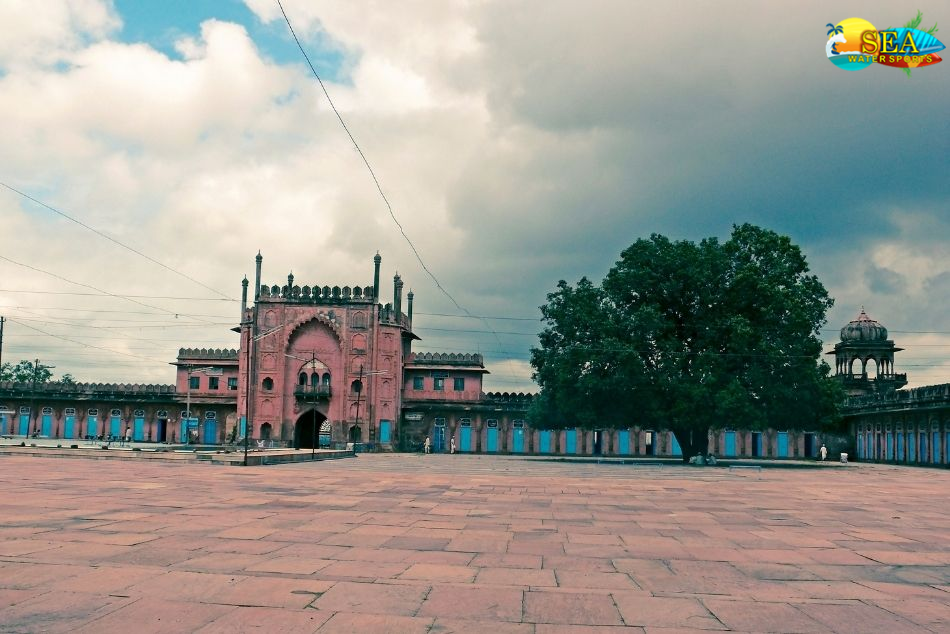
More Places In Madhya Pradesh
Sign In
Sign Up
Use the username and password that you specified when registering on the site
Sign Up
Sign In
Fill in the registration form and save your favorite tours, synchronize them on all devices
Forgot password?
Use the e-mail and password that you specified when registering on the site